Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)
A BRS or bank reconciliation statement is prepared by a company to compare their bank account balance with the accounting records. It helps identify discrepancies between the two data, such as unrecorded transactions, errors, or fraud.
A bank reconciliation statement is an important financial document that helps in tax and financial reporting. It includes details such as deposits, withdrawals and any other transactional activities related to the bank account for a specific period.
Check details on what is bank reconciliation statement, BRS format and the method to prepare a BRS on this page.
Format of Bank Reconciliation Statement
A Bank Reconciliation Statement helps identify and explain the differences between the bank's records and the company's records, ensuring accurate financial reporting. It generally consists of the following components:
- Name of the Company or Account Holder.
- Date of the Statement.
- Bank Balance as per Bank Statement.
- Additions to Bank Statement Balance: This includes deposits in transit, interest earned but not yet recorded by the bank and any other credits not yet recorded by the bank.
- Deductions from Bank Statement Balance: This includes outstanding cheques, bank service charges or fees and any other debits not yet recorded by the bank.
- Adjusted Bank Statement Balance.
- Bank Balance as per Company's Records.
- Any deposits or credits recorded in the company records but not mentioned on the bank statement.
- Deductions from Company's Record Balance.
- Signature of the responsible person who prepared the reconciliation statement.
One can refer to the image below to get a proper understanding of the bank reconciliation statement format.
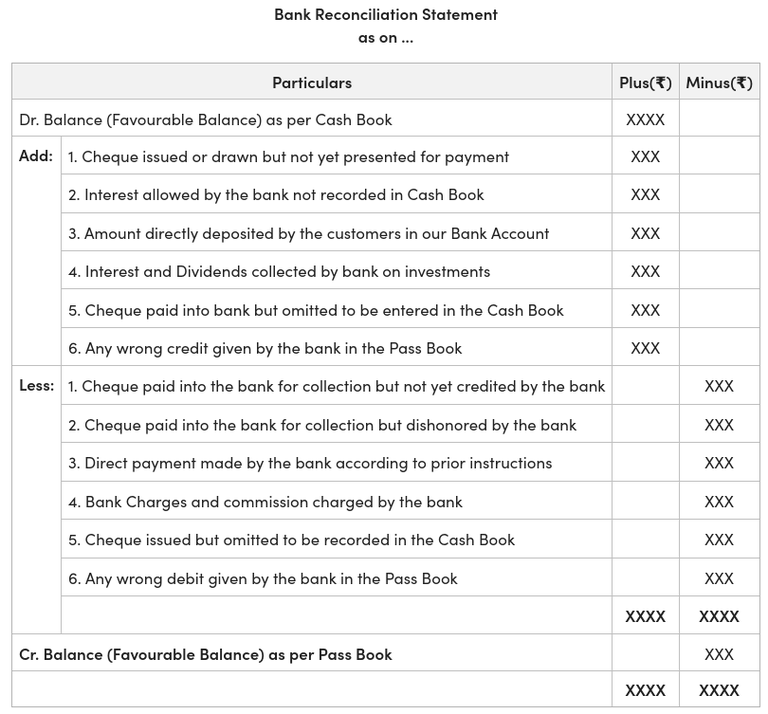
Image source: Geeksforgeeks
Method to Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement
To do the bank reconciliation, one should have their bank statements and accounting records, including chequebooks, receipts, and any deposit slips. Here are the detailed steps to prepare a bank reconciliation statement:
- List outstanding checks: Make a list of any outstanding cheques that have been issued by you but haven't been cleared by the bank.
- Identify deposits in transit: Find any deposits that were made by you but haven't appeared on your bank statement yet. Record these as deposits in transit.
- Compare records: Compare your list of outstanding checks and deposits in transit with the transactions on your bank statement.
- Adjustments: This includes adding deposits in transit to your bank statement balance, deducting outstanding checks from your bank statement balance and considering any bank fees, interest, or errors in your records.
- Reconcile: Calculate the adjusted bank balance and compare it to your own records' balance. They should now match.
- Identify discrepancies: If there are any unresolved discrepancies, investigate and document them. You can contact your bank or review your records to detect any errors.
- Update records: Make any necessary adjustments in your own accounting records to reflect the reconciled balance.
Benefits of Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)
A Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) offers several benefits. Some of the major importance of a BRS are mentioned below:
- It helps identify discrepancies between the company's records and the bank statement, such as accidental errors, omissions, duplications or unauthorised transactions.
- A BRS can uncover fraudulent activities, like unauthorised withdrawals or altered check amounts.
- It ensures the accuracy of a company's financial records, which is important for financial and tax reporting.
- BRS serves as a reference to resolve disputes with the bank regarding fees, interest, or discrepancies in account balances.
- It helps to demonstrate transparency to investors or auditors by showing that financial records are regularly reviewed and reconciled.


